Pure water treatment technology plays a vital role in modern life, ensuring clean and safe water for domestic use, industrial production, and various other sectors. From households to large-scale industrial plants, the demand for high-purity water continues to rise. To meet this need, a range of advanced treatment methods and technologies have been researched and implemented. Let’s explore 6 effective pure water treatment technologies with Đại Nam below!
1. Multimedia Filtration Technology (Sand Filter, Carbon Filter)
Multimedia filtration is a basic yet essential method that uses a filter column filled with multiple layers of media such as gravel, quartz sand, activated carbon, and sometimes specialized materials like manganese sand. As water flows through these layers, suspended solids, sediments, and turbidity are effectively removed. The activated carbon helps absorb residual chlorine, odor-causing organic substances, and improves water clarity.
Key advantages include low investment and operating costs, simple operation, and excellent protection for more sophisticated filtration systems like RO or UF downstream. However, this method mainly targets physical impurities and some basic chemical contaminants—it cannot effectively remove dissolved ions, heavy metals (unless using specific media), or microorganisms.

Multimedia filters effectively remove suspended solids, turbidity, and sediments
2. Ultrafiltration (UF) Technology
Ultrafiltration (UF) uses low-pressure membrane technology with hollow fiber or spiral-wound membranes featuring tiny pore sizes (0.01–0.1 microns). When water is forced through the membrane, small molecules like water and dissolved minerals pass through, while larger particles such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, colloids, and suspended solids are completely retained.
UF advantages include high removal efficiency of microorganisms while retaining beneficial minerals, low energy consumption due to low pressure, and chemical-free operation. However, UF cannot remove dissolved salts or heavy metals and requires good pretreatment to prevent membrane clogging. This technology is widely used in home water purifiers (for mineral retention), pretreatment for RO, industrial water purification, and wastewater reuse.
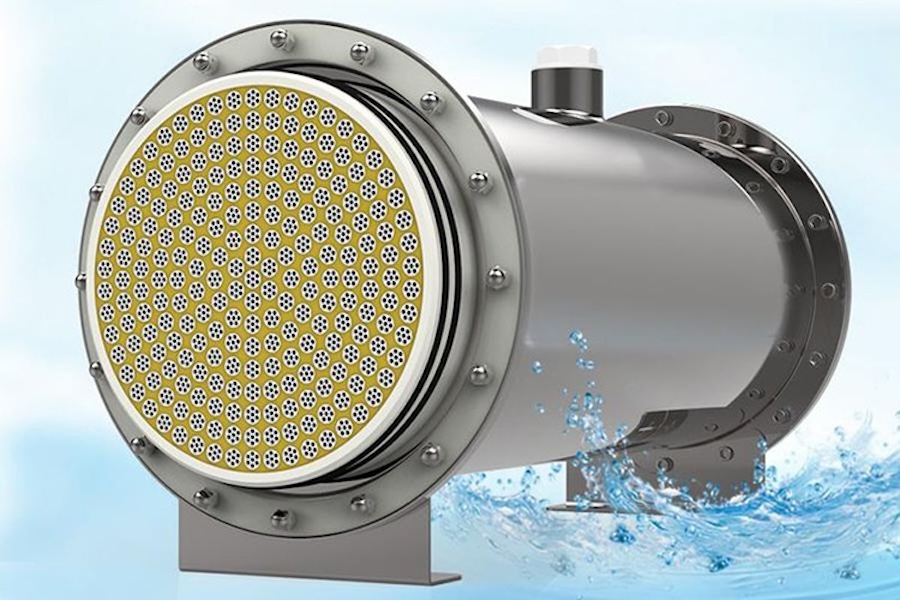

UF membrane modules effectively remove microorganisms while preserving natural minerals in the water
3. Reverse Osmosis (RO) Technology
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is one of the most advanced filtration methods, operating by applying high pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane with an ultra-fine pore size (~0.0001 microns). This process allows water molecules to pass while retaining nearly all other substances, including dissolved salts, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, organic compounds, and harmful chemicals—resulting in highly purified water.
The main advantage of RO is its exceptional filtration efficiency, removing up to 99.9% of TDS and contaminants. It is ideal for bottled drinking water production, ultrapure water in medical, pharmaceutical, and electronics applications, and seawater desalination. However, RO also removes natural minerals, generates a significant amount of wastewater, requires high pressure (thus more energy), and involves higher costs for membranes and pretreatment systems.

Modern RO systems use high-pressure membrane units to produce ultra-pure water
4. Deionization (DI) Technology Using Ion Exchange Resins
Deionization (DI) uses specialized ion exchange resins to remove nearly all dissolved ions (salts, minerals) from water, producing ultra-pure water with extremely high electrical resistance. The system includes both cation and anion resins—cation resin exchanges positive ions (Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺, Na⁺, etc.) with H⁺, and anion resin exchanges negative ions (Cl⁻, SO₄²⁻, etc.) with OH⁻. These ions combine to form pure water (H₂O). DI is often used after RO as a “polishing” step for the highest purity, especially in electronics, semiconductor, pharmaceutical industries, and laboratories.
Advantages include excellent ion removal and resin regenerability. However, it does not remove non-ionic substances or microorganisms. Resin regeneration involves chemical use, leading to higher costs and wastewater treatment requirements.
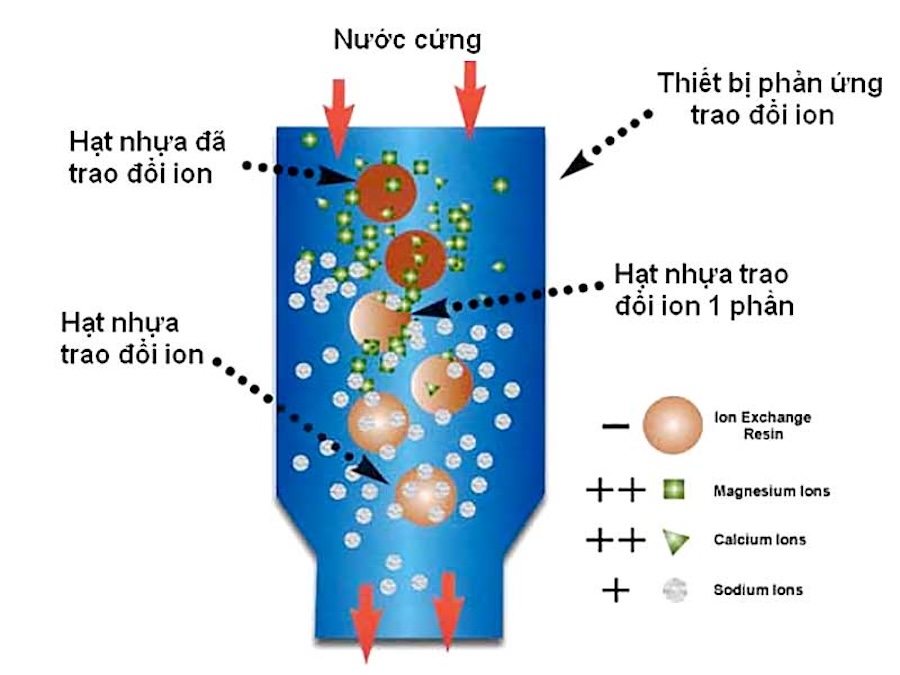
Ion exchange resin columns (DI) are used in ultrapure water systems for industrial applications
5. Ultraviolet (UV) Disinfection Technology
UV disinfection is a safe and effective physical method to eliminate harmful microorganisms in water. The system uses UV-C light at a wavelength of 254 nm directed at the water stream. This light penetrates microbial cell membranes, disrupting their DNA/RNA and rendering them unable to reproduce or cause infections.
Main benefits of UV include effective disinfection (even against chlorine-resistant strains), no chemicals required, no alteration to water’s taste or chemistry, no harmful by-products, and fast, simple operation. However, UV doesn’t remove physical or chemical contaminants (requires clear water input), has no residual effect post-treatment, and requires periodic lamp replacement. UV is commonly used as the final disinfection step in drinking water systems, food and pharmaceutical industries, and treated wastewater.
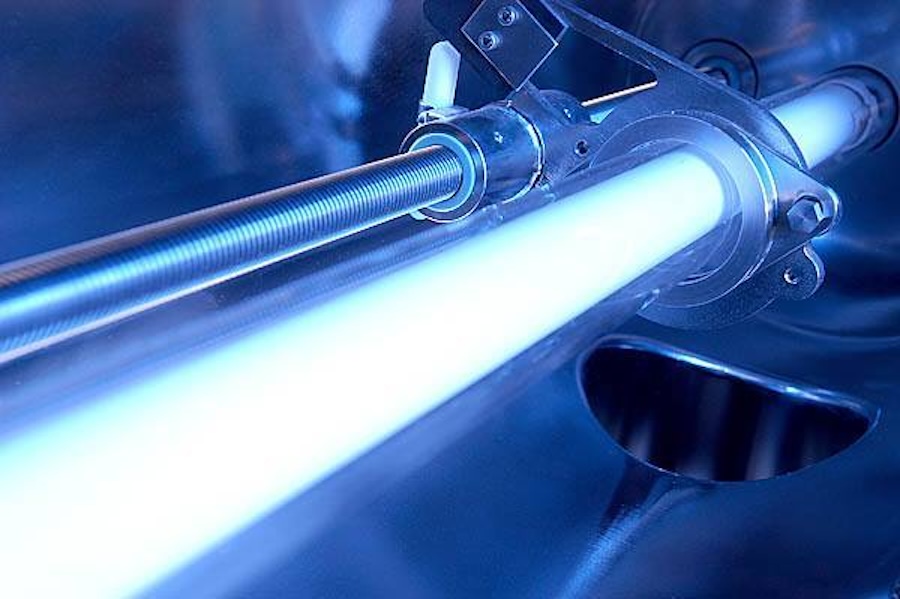

Industrial UV disinfection units offer safe, fast, and chemical-free sterilization
6. Ozone (O₃) Water Treatment Technology
Ozone treatment leverages the strong oxidative power of ozone (O₃) to disinfect, decolorize, deodorize, and break down both organic and inorganic contaminants. Ozone is generated on-site and bubbled into water, where it quickly decomposes into oxygen and reactive oxygen radicals (O•), which attack and destroy microbial membranes (more effectively than chlorine), oxidize dissolved metals (Fe, Mn) into precipitates, and break down complex organic compounds.
Advantages of ozone include superior oxidation and disinfection, no chlorine-based by-products, enhanced water taste and appearance, and increased DO (dissolved oxygen) levels. However, it requires high investment, has no residual disinfection effect, can form bromate if bromide is present, and ozone is toxic—so safety controls are necessary. Ozone is widely used in bottled water production, potable water treatment, industrial wastewater treatment (especially color removal), and swimming pool sanitation.
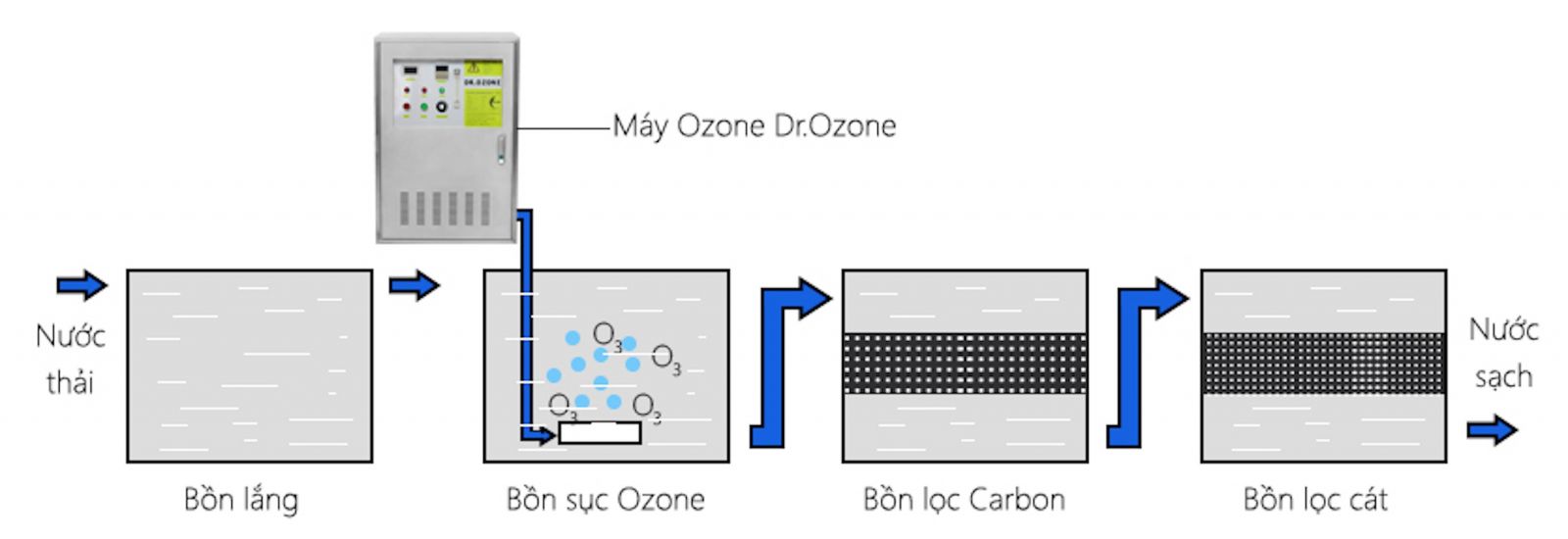
Ozone (O₃) Water Treatment Effectively Removes Organic and Inorganic Contaminants
Each water purification technology comes with its own advantages and limitations, making it suitable for different purposes and water quality requirements. From basic filtration methods like multi-media filters to advanced membrane technologies such as UF, RO, and specialized demineralization and disinfection methods like DI, UV, and Ozone, selecting and combining them effectively is the key to achieving the desired water quality standards. If you're looking for a trusted partner in wastewater treatment system installation or need support with environmental issues, contact Dai Nam today for expert consultation and comprehensive solutions!





